Topic 1: Introduction to Communication
Lesson 5: Communication Barriers and Guidelines for Effectiveness
Despite its importance, communication is often hindered by barriers. Overcoming them requires deliberate strategy and skill.
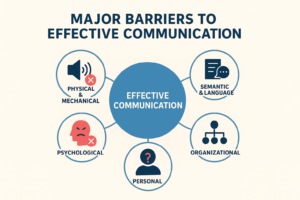
Major Barriers to Effective Communication:
- Physical & Mechanical Barriers: Noise, distance, faulty equipment, power failure.
- Semantic & Language Barriers: Jargon, ambiguous words, different interpretations, language differences.
- Psychological Barriers: Prejudice, emotions (fear, anger), closed-mindedness, status consciousness, distrust.
- Organizational Barriers: Complex hierarchies, restrictive policies, information overload, poor networks.
- Personal Barriers: Poor listening skills, lack of attention, varying perceptions, cultural differences.
Guidelines for Effective Communication (The “How-To”):
- Clarity & Brevity: Be clear in thought and expression. Use simple, concise language.
- Completeness: Ensure the message contains all necessary facts (the 5 Ws: Who, What, When, Where, Why).
- Consideration: Adopt the “you-attitude.” Consider the receiver’s needs, background, and feelings.
- Concreteness: Use specific facts and figures. Avoid vague, abstract language.
- Courtesy: Be polite, respectful, and tactful. Build goodwill.
- Correctness: Ensure factual, grammatical, and technical accuracy.
- Strategic Medium Selection: Match the channel to the message (urgency, complexity, need for record).
- Encourage Feedback: Create an environment where questions and clarifications are welcomed.
- Active Listening: The responsibility is not only on the sender. Receivers must listen attentively and empathetically.
- Manage the Grapevine: Use informal networks positively to supplement formal channels and dispel rumors promptly.