Topic 1: Introduction to Communication
Lesson 3: The Communication Process Model and Its Components
Effective communication can be visualized as a process model, a series of linked steps where each element is crucial for success.
The Communication Process Model:
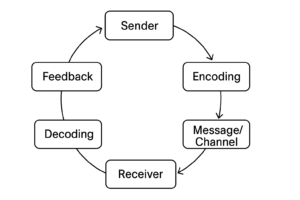
The model consists of a continuous loop: Sender -> Encoding -> Message/Channel -> Receiver -> Decoding -> Feedback -> (back to) Sender.
Detailed Breakdown of Components:
- The Sender (Originator):
- Initiates the process with a need to communicate.
- Responsibilities: Clarifying the idea, encoding it into a clear message, choosing an appropriate medium and channel, and considering the receiver’s background and level of understanding.
- The Message:
- The actual information package (verbal, written, non-verbal) created after encoding.
- It travels through a specific “environment” (e.g., noisy office, formal report, digital network).
- The Medium/Channel:
- The conduit or tool used for transmission.
- Categories: Verbal (oral), Written, Non-Verbal, Visual, Audio-Visual, Electronic.
- Choice depends on urgency, formality, need for record, and audience.
- The Receiver:
- The target audience who decodes the message.
- Decoding is interpreting the symbols (words, signs) back into ideas.
- Effective communication only occurs when the receiver’s understanding aligns with the sender’s intent.
- Feedback:
- The receiver’s response that informs the sender how the message was perceived.
- Critical Function: It confirms understanding, completes the loop, and allows for correction (e.g., retransmission, clarification) if misunderstanding occurs.
- Without feedback, communication is merely “message dumping,” not a two-way process.
Problems in the Communication Process:
- Sender/Receiver Issues: Lack of clarity, poor encoding/decoding skills, preconceptions, fear, cultural differences.
- Channel/Medium Issues: Wrong choice of medium (e.g., email for a sensitive firing), technical failures, information overload/underload.
- Environmental Noise: Physical distractions (sound), psychological noise (stress, emotions), semantic noise (jargon, ambiguous language).